Get started
Pulling from your own system
First, choose and run the utility (options below). The utility:
- connects to your database to pull your schema
- extract 10 sample rows per table
-
capture queries (if
pg_stat_statementsis enabled)
Then, head over to Edit Setup and paste your Postgres connection string.
The analyzer utility powering IndeX-Ray is open source. You can browse the code to see what it does or grab a copy of the zip to run locally. Full instructions below.
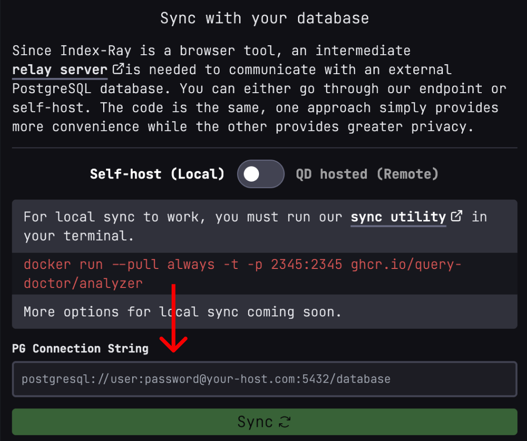
Option 1: Locally, using our Docker image (recommended)
Pre-requisites:
Run docker run --pull always -t -p 2345:2345 ghcr.io/query-doctor/analyzer
Option 2: Locally, running with Docker
Pre-requisites:
Then:
- either:
-
clone via HTTPS
git clone https://github.com/Query-Doctor/analyzer.git, -
or clone via SSH
git clone git@github.com:Query-Doctor/analyzer.git, - or download the source
-
clone via HTTPS
-
docker build -t analyzer . -
docker run -p 2345:2345 analyzer
Option 3: Locally, self-built with Node
Pre-requisites:
Then:
- either:
-
clone via HTTPS
git clone https://github.com/Query-Doctor/analyzer.git, -
or clone via SSH
git clone git@github.com:Query-Doctor/analyzer.git, - or download the source
-
clone via HTTPS
-
deno install -
deno task start
Option 4: Remotely
Select "QD Hosted" (remote)
Note: this only works for remote databases.
Enabling pg_stat_statements (Highly recommended)
To capture query statistics, enable the pg_stat_statements extension. This is optional but recommended for analyzing live queries.
Run this SQL command:
CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS pg_stat_statements; Note: Depending on your setup, you may need to add pg_stat_statements to shared_preload_libraries in your PostgreSQL configuration and restart the server. If you're using an ORM or migration system, you may need to add this as a migration in your codebase.